Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis:
Strong bones start in childhood, but with good habits and healthy food, you can maintain them for life. Bones not only allow us to move and walk, but they also protect our brain, heart, and lungs from injury. But what about osteoporosis and bone fragility.
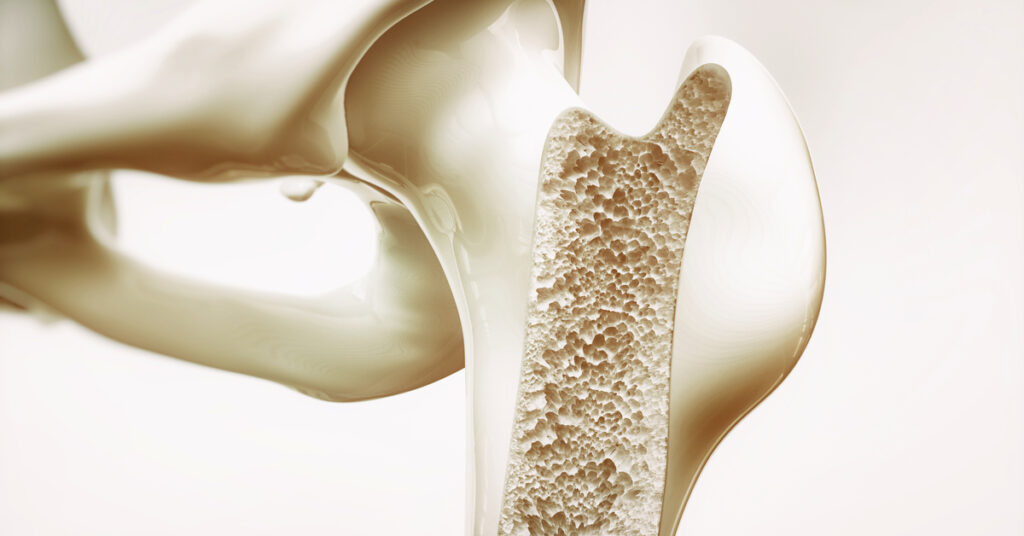
Osteoporosis is a silent disease that starts and progresses before showing any symptoms. In osteoporosis, your bones become fragile, thin, and easy to break. You may not realize you have osteoporosis until you break a bone in a minor incident that would not normally cause a fracture. Osteoporosis occurs when there is a decrease in bone density and mass.
But what causes osteoporosis:
In fact, bones, like other parts of the body, are made up of cells that need nourishment to stay alive. In order to support the body's weight, bones need a strong, mineral-rich structure composed of minerals like calcium and collagen fibers. Bones are constantly renewing themselves; they break down and are replaced with new tissue. Osteoporosis occurs when the rate of bone breakdown exceeds the rate of bone formation, making the bones weak and unable to support the body's weight effectively, so any impact or pressure can cause them to break. There are many factors that make you more susceptible to osteoporosis, such as aging, with women being at higher risk, especially after menopause.
Who is at risk of developing osteoporosis:
1- Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men, but it can also occur in men. Additionally, as age increases, the risk of bone loss also increases. The frequency of osteoporosis may vary by ethnicity: white and Asian women are at higher risk, while African-American and Mexican-American women have lower risks.
2- The most important factor is the dietary pattern, as calcium-poor foods increase the risk of osteoporosis. Calcium is abundant in bones and gives them strength and resilience, but it is also essential for other parts of the body such as muscles and nerves. When there is a deficiency due to inadequate dietary intake, the body withdraws calcium from the bones under the influence of a certain hormone (increasing bone breakdown at the expense of its formation), leading to weakened bone structure.
3- Family history also plays a role; the risk of developing osteoporosis may be higher if one of your parents has osteoporosis or a hip fracture.
4- Hormonal changes can increase your risk of developing osteoporosis.
5- Taking certain medications can expose you to the risk of osteoporosis: corticosteroids, proton pump inhibitors (used for acid reflux), seizure medications, cancer treatments (radiation and chemotherapy), suppression of reproductive hormones, immune-suppressing agents.
6- Certain diseases can increase your risk of osteoporosis: endocrine disorders, some digestive system diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, certain types of cancer, HIV, anorexia nervosa, chronic lung diseases.
7- Alcohol consumption (having more than two alcoholic drinks several times a week) can also increase your risk.
Diagnosis of osteoporosis:
Certain individuals should undergo routine screening to prevent osteoporosis and its associated problems: women over the age of 65, women of any age with risk factors for developing osteoporosis. Additionally, those with predisposing factors should also be screened, as osteoporosis does not present clear symptoms that prompt a visit to the doctor.
For men, international organizations do not recommend routine screenings due to the presence of male hormones throughout their lives, which provide a certain level of bone stability. In contrast, women are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis due to a decrease in estrogen levels during menopause. Therefore, women should regularly visit bone clinics.
The doctor will need the following information:
- Medical history/occurrence of bone fractures/history of occurrence.
- A physical examination may be conducted, which may include checking for:
- Loss of height and/or weight
- Changes in posture
- Balance and gait
- Muscle strength
- Bone density testing may be requested; this test is quick (5 to 10 minutes), safe, and painless. Your doctor may also want to conduct a blood test to check for vitamin D deficiency or abnormal calcium levels.