Gingivitis
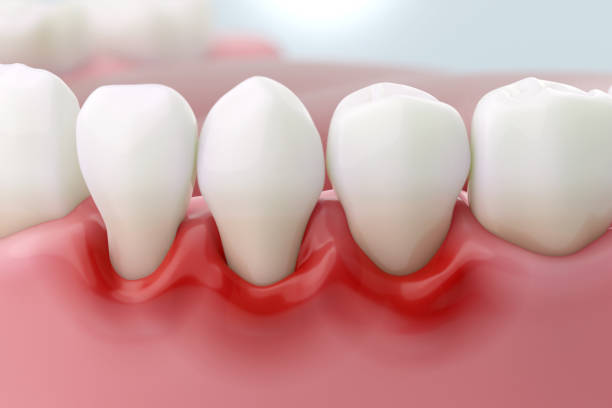
Gingivitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment at Home and the Dentist
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease (the gums are the pink tissue surrounding your teeth). It occurs due to the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth and gums, leading to irritation, redness, and swelling of the gums. Although early-stage gingivitis is usually not painful, it can progress to a more serious condition called periodontitis if left untreated. It is also one of the most common causes of bleeding gums in adults.
Causes of Gingivitis:
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing lead to plaque buildup, which causes gum inflammation.
- Smoking: A major factor that weakens the immune system and increases the risk of chronic gingivitis.
- Hormonal changes: Such as during pregnancy or puberty, when gums become more sensitive and prone to swelling and bleeding.
- Chronic illnesses: Like diabetes or autoimmune diseases, which reduce the body’s defense against bacteria in the gums.
- Certain medications: Such as blood pressure drugs and antibiotics, which can affect gum health.
- Vitamin deficiencies: Especially vitamin C, which is essential for healthy tissue repair and helps prevent receding or bleeding gums.
Symptoms of Gingivitis:
1- Red and swollen gums (a common early sign of gingivitis).
2- Gums that bleed while brushing or flossing.
3- Persistent bad breath (halitosis is a frequent sign of gum infection)
4- Gum recession (gums pulling away from the teeth)
5- Mild pain or discomfort while chewing
If you notice any of these gingivitis symptoms, it’s important to address them early to prevent complications.
Gingivitis Treatment:
- Home Care Routine
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste — a key part of at-home gingivitis treatment.
- Floss daily to remove plaque from between the teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash such as chlorhexidine to help remove bacteria from the gums and reduce inflammation.
- Dental Clinic Treatment
- Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) to remove plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
- Antibiotics (topical or oral) may be prescribed for more persistent infections.
- Surgical treatment may be necessary in advanced cases to repair damaged gum and bone tissue.
Preventing Gingivitis:
1- Maintain daily oral hygiene to prevent plaque buildup.
2- Visit your dentist regularly (at least every 6 months) for checkups and professional cleanings.
3- Quit smoking, which is a key risk factor for gum bleeding and gum disease.
4- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins, especially vitamin C.
5- Reduce stress, as it can weaken your immune system and worsen gum problems.
Summary:
Gingivitis is a common but preventable and treatable condition. Good oral hygiene and healthy habits can go a long way in protecting your gums. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can stop the condition from progressing to serious gum disease that can affect the teeth and supporting bone.
If you experience any symptoms mentioned above, don’t delay a visit to your dentist.

Dr. Dima AL BATAL

Batool Al Naser

Dr. Hassan Alghawi

Dr. Ashraf Nouman

Dr. Patrick Azir

Dr. Alaa Hishmeh

Dr. América Escandón

Dr. Ismail Madookh

Dr. Wahb Ziyoud

Dr. Rana Malouk

Dr. Aiham Matanes

Dr Mansour Masoumi

Dr. Ahmed El-Sawy

Dr. Habib Dezhagah

Dr. Noha Haider

Ahed sarraj

Dr. Radwan Sallam

Dr. Amina Al-Asali

Dr. Molham Hassoun

Dr.osama almoree

Dr. Amira Abdelrahim Elgak Hassan

Dr. Nadin Merza

Dr. Mira Hamed

Dr. Sami George

Dr. Hayat Muin Ismail

Dr. Majda Mohamed Khair Abdo

Dr. Mohamed Helmi Hussine

Dr. Ossama Mesbah Zaher

Dr. Ammar AL Farhan

Dr. Nidal Habbak

Dr. Rachid Al-Kudsi Sabbagh

Dr. Ahmad Qara Ali

Dr. Abdul Jabbar Al Sobh

Dr.Mais Zarzar

Dr. Yara Alhasibi

Dr. Fadi Nageeb

Dr. Assef Ahmad
