Tooth Decay
Best Services In The Area
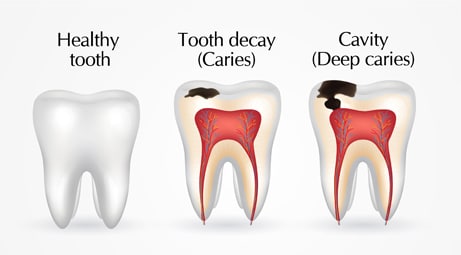
Tooth Decay: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Introduction
Oral and dental health is a vital part of overall well-being. Tooth decay is one of the most common dental problems affecting both children and adults. It begins when acids, produced by bacteria in the mouth, attack the tooth enamel. If left untreated, decay can spread deeper into the tooth, leading to serious complications.
What Is Tooth Decay?
Tooth decay is the breakdown of tooth structure caused by acids produced by bacteria feeding on sugars and carbohydrates left on the teeth. Over time, these acids erode the enamel and may reach the inner layers of the tooth.
Causes of Tooth Decay
Several factors can contribute to the development of cavities, including:
1- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly leads to plaque buildup.
2- Frequent consumption of sugary foods and drinks: Especially sweets and soda.
3- Inadequate water intake, particularly water lacking fluoride.
4- Dry mouth: Often caused by certain medications or health conditions.
5- Genetics: Some individuals are more prone to decay due to inherited traits.
Symptoms of Tooth Decay:
Common signs of tooth decay include:
1-Toothache or pain when eating sweet, hot, or cold food.
2- Visible holes or dark/brown spots on teeth.
3- Persistent bad breath.
4- Tooth sensitivity.
5- Swollen gums or pus in cases of advanced decay.
Complications of Untreated Cavities:
If not treated, tooth decay can lead to:
1- Infection of the pulp (nerve) of the tooth.
2- Dental abscess (pus-filled infection).
3- Complete tooth loss.
4- Spread of infection to other parts of the body in severe cases.
How to Prevent Tooth Decay:
To maintain a healthy smile and prevent cavities, follow these tips:
1- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
2- Use dental floss or interdental brushes daily.
3- Visit your dentist regularly (every 6 months).
4- Limit intake of sugary snacks and starchy foods.
5- Drink plenty of water, especially after meals.
6- For children, consider fluoride treatments or sealants for added protection.
Treatment Options for Tooth Decay:
Treatment depends on how advanced the decay is:
- Early stage: Fluoride treatments may help remineralizer the enamel.
- Mild decay: The cavity is cleaned and filled with dental material.
- Advanced decay: Root canal therapy is needed if the nerve is affected.
- Severe damage: The tooth may need to be extracted.
Conclusion:
Tooth decay is a preventable condition, but ignoring it can lead to serious dental and health issues. Good oral hygiene and routine dental check-ups are key to keeping your teeth healthy and your smile bright.
Dr. Ashraf Nouman

Dr. Patrick Azir

Dr. Alaa Hishmeh

Dr. América Escandón

Dr. Ismail Madookh

Dr. Wahb Ziyoud

Dr. Rana Malouk

Dr. Firas Dib

Dr. Aiham Matanes

Dr Mansour Masoumi

Dr. Bassem Al Hussein

Dr. Elaf Mansour

Dr. Ghassan Al-Tawil

Dr. Ahmed El-Sawy

Dr. Rafeh Al-Hameed

Dr. Habib Dezhagah

Tasnim Yahia

Dr. Noha Haider

Dr.Abdulrhman Snttiha

Ahed sarraj

Dr. Radwan Sallam

Dr. Alaa Hakim

Dr. Amina Al-Asali

Dr. Hassan Al Tawil

Dr. Ghina Kogan

Dr Abdulrahman Alfakir

Dr Nizar Farwati

Dr. Huda Zahra

Dr. Molham Hassoun

DR.Talah Alrayes

Dr.Asmaa Alsaleem

Dr. Ayas Alaraki

Dr.osama almoree

Dr. Mohammed kenj

Doctor Sabreen Al Salem

Dr. Amira Abdelrahim Elgak Hassan

Dr. Nadin Merza

Dr. Mohammad Al balawai

Dr. Yasmin Tohme

Dr. Mira Hamed

Dr. Sami George

Dr. Adham Mansour

Dr. Mahyar Moutwwag

Dr. Hayat Muin Ismail

Dr. Azzam Aslan

Dr. Belal Rahima

Dr. Qusai Darwish

Dr. Majda Mohamed Khair Abdo

Dr. Ali Hassan

Dr. Naim Sarkis Satme

Dr. Mohamed Helmi Hussine

Dr. Ossama Mesbah Zaher

Dr. Ammar AL Farhan

Dr. Aya Sabsabi AlRifae

Dr. Mohammad Hayem Zin Alabdin

Dr. Nidal Habbak

Dr. Rachid Al-Kudsi Sabbagh

Dr. Amr Arafa

Dr. Majd Habeeb

Dr. Ahmad Qara Ali

Dr. Laila Al-Bahri

Dr. Abdul Jabbar Al Sobh

Dr. Lama Beshri

Dr. Asma Alghawi

Dr.Mais Zarzar

Dr. Ghada Satouf

Dr. Majd Al Farra

Dr. Yara Alhasibi

Dr. Fadi Nageeb

Dr. Assef Ahmad

Dr. Abdulrahman Al-Jabi

Dr. Mohammad Wahib Wahbeh

Dr. Samer Hijjo
